New technology suggests Shroud of Turin is 2,000 years old
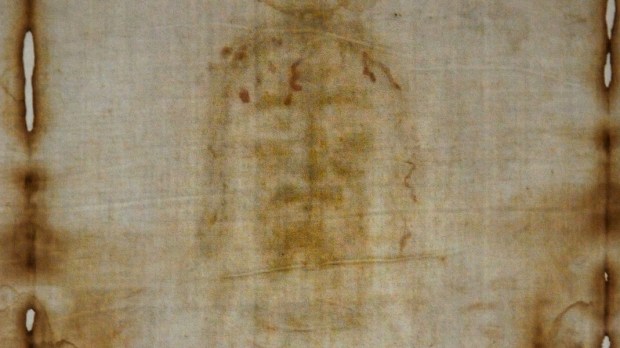
In 1988 radiocarbon dating of the Shroud of Turin found that the relic many faithful believe to be the burial linen of Christ originated about 700 years ago. While the study suggested the shroud was not authentic, it has done little to abate the faith of those thousands who make pilgrimage to Turin to venerate the relic. Now, a new dating technology has placed the fabric within the time of Christ.
WAXS
The study was conducted by Dr. Liberato de Caro of Italy’s Institute of Crystallography of the National Research Council, in Bari. Dr. de Caro has employed a method known as “Wide-Angle X-ray Scattering,” or WAXS, which measures the natural aging of flax cellulose and converts it to time since manufacture.
The process has several key features that make it more desirable than radiocarbon dating, not least of which that it is completely non-destructive to the samples. Furthermore, the size of the sample required for WAXS is much smaller, requiring just a portion of cloth approximately 0.5mm x 1mm.
Carbon-14 inadequacy
In his report, published on the website of Italy’s Department of Chemical Sciences and Materials Technologies, de Caro pointed out a few flaws with dating by Carbon-14 analysis. He noted that textile samples can easily become contaminated with substances that could skew its results. He wrote:
“Molds and bacteria, colonizing textile fibers, and dirt or carbon-containing minerals, such as limestone, adhering to them, in the empty spaces between the fibers that at a microscopic level represent about 50% of the volume, can be so difficult to completely eliminate in the sample cleaning phase, which can distort the dating.”
De Caro noted that fabric can even become enriched with new Carbon-14 samples. At this point, it would become hard to identify if carbon dating measured the original fabric, or a layer of carbon that was accumulated over time.
WAXS Dating
De Caro explained that the WAXS method was used on a variety of samples of historical textiles that have been documented to be aged from 3000 BC to 2000 AD. He placed the Shroud of Turin against these samples and found that it best matched a piece of fabric known to have come from the siege of Masada, Israel, in 55-74 AD.
If accurate, the findings would suggest that the shroud originated around the time of Christ, and this could mean it was indeed Jesus’ burial cloth. Still, de Caro has advised caution, as the new date contrasts the Carbon-14 dating by such a large margin.
Dr. de Caro suggested that the WAXS analysis should be performed by other laboratories in order to confirm the findings. In an interview with National Catholic Register, he said:
“The technique of dating linen by X-ray is non-destructive. Therefore, it can be repeated several times on the same sample… it would be more than desirable to have a collection of X-ray measurements carried out by several laboratories, on several samples, at most millimetric in size, taken from the Shroud.”
Pollen
De Caro also noted some exciting elements that could help trace the shroud’s history and migration from the Middle East to Europe. He noted that the samples of the shroud contained samples of pollen from the ancient region of Palestine, which could not have originated in Europe. This factor alone suggests that the Shroud of Turin spent extensive time in the Middle East.
Read de Caro’s full report on his WAXS analysis of the Shroud of Turin, here.
Click here to read his full interview with NCR.
"WAXS, which measures the natural aging of flax cellulose and converts it to time since manufacture."
ReplyDeleteHow odd. according to peer reviewed scientific papers
"Wide Angle X-ray Scattering (WAXS) is a technique used for the investigation of partially ordered materials. It is often employed to characterise the crystalline structure of polymers, by measuring the interatomic spacings within the unit cell. It is sub-nanometre-sized structures within the sample that cause the wide angles."
Nothing there about fabric, aging or dating. Very fishy.